Word 2 Vector
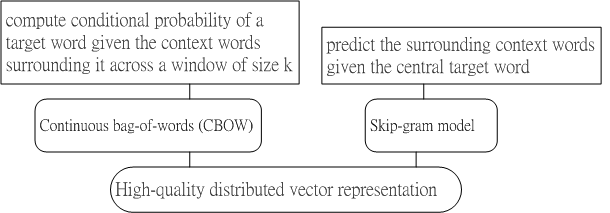
Fig.1 CBOW and skip gram Model are two high-quality distributed vector representation
Fig.1 shows the schematic for CBOW and skip gram model.
CBOW and skip-gram models was proposed as a revolution of word embeddings [1].
CBOW computes the conditional probability of a target word given the context words surrounding it across a window of size k.
The skip-gram model does the exact opposite of the CBOW model, by predicting the surrounding context words given the central target word.
The context words are assumed to be located symmetrically to the target words within a distance equal to the window size in both directions.
Considering a simplified version of the CBOW model where only one word is considered in the context. This essentially replicates a bigram language model.
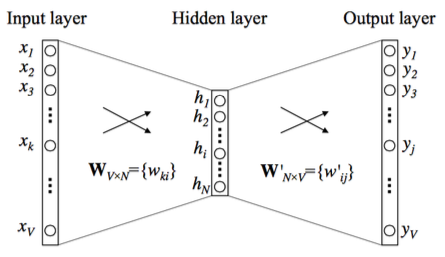
Fig.2 CBOW model, as a connected neural network with one hidden layer.
Fig.2 shows the CBOW model, which is a fully connected neural network with one hidden layer.
The input layer takes the one-hot vector of context word, and has V neurons while the hidden layer has $N$ neurons. The output layer is softmax of all words in the vocabulary.
[0]
Young, Tom, et al. "Recent trends in deep learning based natural language processing." arXiv preprint arXiv:1708.02709 (2017).
[1]
T. Mikolov, K. Chen, G. Corrado, and J. Dean, ¡§Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space,¡¨ arXiv preprint arXiv:1301.3781, 2013.