Silence Removal and Event Detection
Function silenceRemoval() from audioSegmentation.py takes an un-iterrupted audio recording as input and return segments endpoints corresponding to individual audio events. All "silent" areas of the signal are removed.
Function silenceRemoval() use a semi-supervised approach
- an SVM model is trained to distinguish between high-energy and low-energy short-term frames. 10% of the highest energy frames along with 10% of the lowest ones are used in training.
- the SVM model with a probabilistic output is applied on whole recording and a dynamic thresholding is used to detect the active segments
Usage example
from pyAudioAnalysis import audioBasicIO as aIO
from pyAudioAnalysis import audioSegmentation as aS
[Fs, x] = aIO.readAudioFile("data/recording1.wav")
segments = aS.silenceRemoval(x, Fs, 0.020, 0.020, smoothWindow = 1.0, Weight = 0.3, plot = True)
segments is a list of segments endpoints.
Each endpoint has two elements, segment beginning and segment ending (in seconds).
Command-Line Usage Example
指令1 python audioAnalysis.py silenceRemoval -i data/recording3.wav --smoothing 1.0 --weight 0.3
指令2 python audioAnalysis.py classifyFolder -i data/recording3_ --model svm --classifier data/svmSM --detail
指令1 把data/recording3.wav裁減出很多以data/recording3_開的segment檔。
指令2 把data/recording3_的segment檔用事先訓練好的data/svmSM svm model是屬於speech或music。
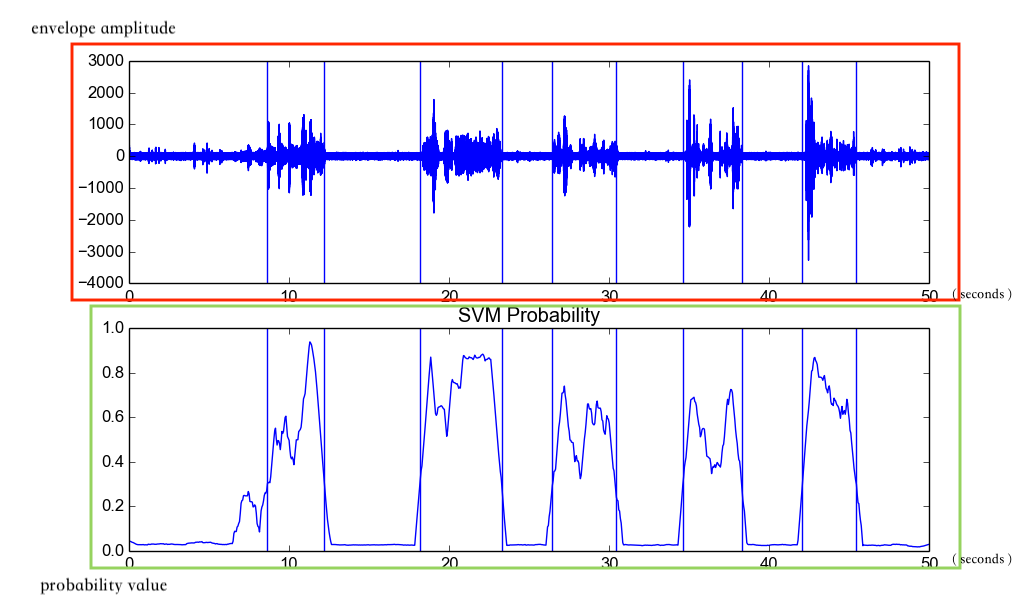 Figure 2
Figure 2 silenceRemoval() result of data/recording3.wav
Figure 2 說明函數silenceRemoval()處理音頻data/recording3.wav的結果。
Figure 2(紅)顯示音頻data/recording3.wav的波形圖。橫軸是時間軸,單位是秒;縱軸是波包(envelope)的強度。垂直線是segment的邊界(boundary)在,在第一條跟第二條垂直線中間是第一個active segment,第三條跟第四條垂直線中間是第二個active segment,以此類推,在第跟第垂直線中間是第個active segment。其他非active segment就是所謂的silence segment。
Figure 2(橙)顯示音頻data/recording3.wav是active segment的機率圖。橫軸是時間軸,單位是秒;縱軸是機率值。垂直線跟Figure 2(紅)一樣是segment的邊界。
In rather sparse recordings (i.e. the silent periods are quite long), longer smoothing window and a looser probability threshold are used.
In continuous recording, a shorter smooth window and a stricter probability threshold are used.
continuos recording example
python audioAnalysis.py silenceRemoval -i data/count2.wav --smoothing 0.1 --weight 0.6
Source Code
 Figure 3
Figure 3
def silenceRemoval(x, Fs, stWin, stStep, smoothWindow=0.5, Weight=0.5, plot=False):
'''
Event Detection (silence removal)
ARGUMENTS:
- x: the input audio signal
- Fs: sampling freq
- stWin, stStep: window size and step in seconds
- smoothWindow: (optinal) smooth window (in seconds)
- Weight: (optinal) weight factor (0 < Weight < 1) the higher, the more strict
- plot: (optinal) True if results are to be plotted
RETURNS:
- segmentLimits: list of segment limits in seconds (e.g [[0.1, 0.9], [1.4, 3.0]] means that
the resulting segments are (0.1 - 0.9) seconds and (1.4, 3.0) seconds
'''
if Weight >= 1:
Weight = 0.99
if Weight <= 0:
Weight = 0.01
# Step 1: feature extraction
x = audioBasicIO.stereo2mono(x) # convert to mono
ShortTermFeatures = aF.stFeatureExtraction(x, Fs, stWin * Fs, stStep * Fs) # extract short-term features
# Step 2: train binary SVM classifier of low vs high energy frames
EnergySt = ShortTermFeatures[1, :] # keep only the energy short-term sequence (2nd feature)
E = numpy.sort(EnergySt) # sort the energy feature values:
L1 = int(len(E) / 10) # number of 10% of the total short-term windows
T1 = numpy.mean(E[0:L1]) + 0.000000000000001 # compute "lower" 10% energy threshold
T2 = numpy.mean(E[-L1:-1]) + 0.000000000000001 # compute "higher" 10% energy threshold
Class1 = ShortTermFeatures[:, numpy.where(EnergySt <= T1)[0]] # get all features that correspond to low energy
Class2 = ShortTermFeatures[:, numpy.where(EnergySt >= T2)[0]] # get all features that correspond to high energy
featuresSS = [Class1.T, Class2.T] # form the binary classification task and ...
[featuresNormSS, MEANSS, STDSS] = aT.normalizeFeatures(featuresSS) # normalize and ...
SVM = aT.trainSVM(featuresNormSS, 1.0) # train the respective SVM probabilistic model (ONSET vs SILENCE)
# Step 3: compute onset probability based on the trained SVM
ProbOnset = []
for i in range(ShortTermFeatures.shape[1]): # for each frame
curFV = (ShortTermFeatures[:, i] - MEANSS) / STDSS # normalize feature vector
ProbOnset.append(SVM.predict_proba(curFV.reshape(1,-1))[0][1]) # get SVM probability (that it belongs to the ONSET class)
ProbOnset = numpy.array(ProbOnset)
ProbOnset = smoothMovingAvg(ProbOnset, smoothWindow / stStep) # smooth probability
# Step 4A: detect onset frame indices:
ProbOnsetSorted = numpy.sort(ProbOnset) # find probability Threshold as a weighted average of top 10% and lower 10% of the values
Nt = ProbOnsetSorted.shape[0] / 10
T = (numpy.mean((1 - Weight) * ProbOnsetSorted[0:Nt]) + Weight * numpy.mean(ProbOnsetSorted[-Nt::]))
MaxIdx = numpy.where(ProbOnset > T)[0] # get the indices of the frames that satisfy the thresholding
i = 0
timeClusters = []
segmentLimits = []
# Step 4B: group frame indices to onset segments
while i < len(MaxIdx): # for each of the detected onset indices
curCluster = [MaxIdx[i]]
if i == len(MaxIdx)-1:
break
while MaxIdx[i+1] - curCluster[-1] <= 2:
curCluster.append(MaxIdx[i+1])
i += 1
if i == len(MaxIdx)-1:
break
i += 1
timeClusters.append(curCluster)
segmentLimits.append([curCluster[0] * stStep, curCluster[-1] * stStep])
# Step 5: Post process: remove very small segments:
minDuration = 0.2
segmentLimits2 = []
for s in segmentLimits:
if s[1] - s[0] > minDuration:
segmentLimits2.append(s)
segmentLimits = segmentLimits2
if plot:
timeX = numpy.arange(0, x.shape[0] / float(Fs), 1.0 / Fs)
plt.subplot(2, 1, 1)
plt.plot(timeX, x)
for s in segmentLimits:
plt.axvline(x=s[0])
plt.axvline(x=s[1])
plt.subplot(2, 1, 2)
plt.plot(numpy.arange(0, ProbOnset.shape[0] * stStep, stStep), ProbOnset)
plt.title('Signal')
for s in segmentLimits:
plt.axvline(x=s[0])
plt.axvline(x=s[1])
plt.title('SVM Probability')
plt.show()
return segmentLimits
[0] https://github.com/tyiannak/pyAudioAnalysis/wiki/5.-Segmentation
[1] Giannakopoulos, Theodoros, and Sergios Petridis. "Fisher linear semi-discriminant analysis for speaker diarization." IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing 20.7 (2012): 1913-1922.